How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, bridging the gap between technological advancement and practical application. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and legal considerations to advanced flight maneuvers and photography techniques. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, navigating different flight modes, and capturing stunning aerial footage. Crucially, we will also emphasize the importance of responsible drone operation, adhering to safety protocols, and respecting legal regulations. By the end of this guide, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to operate a drone responsibly and effectively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before launching your drone, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful operation. This involves inspecting various components and understanding relevant regulations. Failure to do so could result in accidents or legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition for flight. This systematic approach minimizes the risk of malfunctions during operation.
| Component | Check | Component | Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or loose attachment. | Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s securely connected. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any signs of damage or debris. | GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Gimbal | Ensure the gimbal moves smoothly and is properly calibrated. |
| Airframe | Check for any damage or loose parts on the drone’s body. | Flight Controller | Confirm the flight controller is functioning correctly. |
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to local laws and regulations. Understanding airspace restrictions is paramount to avoid legal issues and potential accidents.
- Register your drone with the relevant authorities (if required in your region).
- Check for temporary flight restrictions (TFRs) in your area, often related to events or emergencies.
- Maintain awareness of no-fly zones, such as airports, military bases, and prisons.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
Safe Drone Launch Procedure
A safe and controlled launch is essential for preventing accidents. Following these steps will ensure a smooth takeoff.
- Find a suitable, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone’s remote controller first, followed by the drone itself.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (if applicable).
- Perform a pre-flight check of the drone’s systems.
- Slowly lift the drone off the ground using the throttle control.
- Hover for a few seconds to ensure stability before commencing flight.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation techniques is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explain the basic controls and various flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones use a similar set of controls. Mastering these is fundamental to piloting.
- Throttle: Controls the altitude of the drone (up and down).
- Yaw: Rotates the drone left or right (around its vertical axis).
- Pitch: Tilts the drone forward or backward.
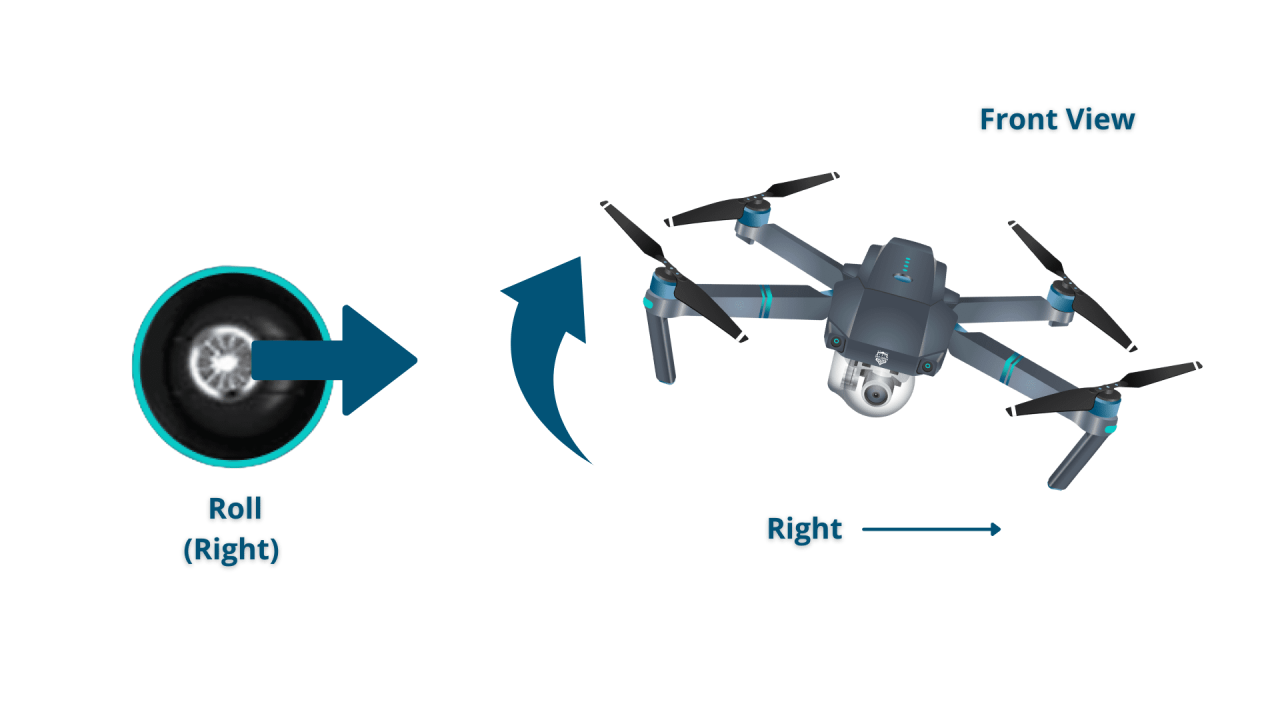
- Roll: Tilts the drone left or right.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Choosing the appropriate mode depends on the flight situation.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stable hovering. Ideal for beginners and long-distance flights.
- Attitude Mode: Relies on the drone’s internal sensors for orientation and control. Provides more responsive maneuvering but requires more skill.
- Manual Mode (or other advanced modes): Offers full control over the drone’s movements but demands significant experience and skill.
Drone Navigation Using GPS Coordinates and Waypoints
Modern drones allow for precise navigation using GPS coordinates and pre-programmed waypoints. This enables autonomous flights and complex maneuvers.
By inputting GPS coordinates into the drone’s flight controller, you can direct it to specific locations. Similarly, waypoints can be set to create a flight path for automated missions. Many drone apps allow for easy waypoint creation and management.
Flight Techniques and Maneuvers
Proficient drone operation involves mastering various flight maneuvers. Practice is key to developing smooth and controlled flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting. Practice each one until you feel comfortable.
- Taking Off: A smooth, controlled ascent to a safe hovering altitude.
- Landing: A gradual descent to a soft landing on a stable surface.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Moving in Different Directions: Precisely controlling the drone’s movement using pitch, roll, and yaw.
Flight in Various Conditions
Adapting to different environmental conditions is essential for safe drone operation. Windy conditions and confined spaces present unique challenges.
- Windy Conditions: Reduce speed and maintain a stable hover. Use more precise control inputs.
- Confined Spaces: Fly slowly and deliberately, paying close attention to obstacles.
Demonstrative Flight Maneuvers
A series of maneuvers showcasing proficiency includes transitions between altitudes and directional changes.
- Ascend to a predetermined altitude.
- Hover for a few seconds.
- Perform a 360-degree yaw rotation.
- Descend to a lower altitude.
- Transition between different altitudes several times.
- Move in different directions (forward, backward, left, right).
Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
The camera is a key feature of many drones. Understanding its settings and techniques allows you to capture high-quality images and videos.
Drone Camera Settings
Familiarize yourself with these settings to control the look and feel of your shots.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the camera’s sensor to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light that enters the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
- Shooting Modes: Many drones offer various shooting modes like photo, video, timelapse, and panorama.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Tips for optimal image and video capture.
- Use a tripod or other stabilizing device for still shots.
- Shoot in RAW format for greater editing flexibility (if your drone supports it).
- Use a neutral density (ND) filter to reduce the amount of light entering the lens, allowing for wider apertures and slower shutter speeds.
- Pay attention to lighting conditions and try to shoot during the golden hour for the best light.
Composing Shots Using the Drone’s Camera
Strategic shot composition elevates the quality of your drone footage.
- Plan your shots beforehand, considering the angle, perspective, and subject matter.
- Use the drone’s camera to explore different angles and perspectives.
- Experiment with different compositions, such as rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry.
- Maintain a steady hand and avoid jerky movements.
| Scenario | ISO | Shutter Speed | Aperture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Sunlight | 100 | 1/250s | f/5.6 |
| Overcast | 200 | 1/125s | f/4 |
| Low Light | 800 | 1/60s | f/2.8 |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems is essential.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes

Identifying the source of the problem is the first step towards resolution.
- Low Battery: Insufficient charge, excessive use, or battery degradation.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions, interference, or weak signal strength.
- Motor Failure: Mechanical damage, overheating, or electrical issues.
- Connection Loss: Interference, distance from the controller, or radio frequency issues.
Solutions for Common Drone Problems, How to operate a drone
Quick fixes and steps to address common issues.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before the next flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception, recalibrate the compass.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage, consider replacement if necessary.
- Connection Loss: Reduce the distance from the drone, ensure there’s no interference.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A visual representation of troubleshooting steps (described below, as requested to avoid actual image usage).
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic flight maneuvers. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with safety regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, consistent practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Imagine a flowchart starting with a “Problem Detected” box. Branches lead to specific problems (low battery, GPS loss, etc.). Each problem branch has a series of troubleshooting steps represented by boxes connected by arrows. For example, the “low battery” branch would have boxes like “Check battery level,” “Charge battery,” “Replace battery if needed,” leading to a final “Problem Solved” or “Problem persists” box.
The “GPS loss” branch would similarly guide the user through checking GPS signal strength, recalibrating the compass, and relocating to a clear area. The flowchart would then converge to a final “Problem Solved” or “Seek professional help” box.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and routine maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued safe operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively navigate your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This site provides comprehensive guidance on everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared before taking to the skies with your drone.
Safe Landing and Storage
These steps ensure your drone is safely returned to the ground and stored appropriately.
- Gradually descend the drone to a safe landing area.
- Power off the drone and the controller.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Store the drone in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance keeps your drone in optimal working condition.
- Cleaning: Gently wipe down the drone’s body and propellers with a soft cloth.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging them.
- Propeller Inspection: Regularly check for damage or wear and tear.
Post-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive checklist simplifies post-flight tasks.
- Safe landing
- Power off drone and controller
- Inspect for damage
- Clean the drone
- Charge batteries
- Store drone and accessories properly
Understanding Drone Batteries and Flight Time: How To Operate A Drone
Drone batteries are crucial for flight duration. Understanding their care and limitations is essential.
Proper Battery Care and Charging
Proper battery care ensures optimal performance and longevity.
- Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
- Avoid overcharging or fully discharging the battery.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Monitor battery health using the drone’s software or a dedicated battery analyzer.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Various factors influence how long your drone can stay airborne.
- Weather Conditions: Wind and temperature significantly impact flight time.
- Payload: Heavier payloads consume more battery power.
- Flight Style: Aggressive maneuvers and high speeds drain the battery faster.
Calculating Flight Time
Calculating flight time involves considering battery capacity and drone consumption rate.
Flight time can be estimated by dividing the battery’s capacity (in mAh) by the drone’s average current draw (in mA). For example, a drone with a 5000mAh battery and an average current draw of 500mA would have an estimated flight time of 10 hours (5000mAh / 500mA = 10 hours). However, this is a theoretical calculation. Actual flight time may vary due to factors mentioned above.
Drone Safety and Responsible Operation
Responsible drone operation prioritizes safety and ethical considerations. This section Artikels key aspects of safe and legal drone use.
Ethical Considerations
Respecting others’ privacy and airspace is paramount.
- Avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Do not record or photograph people without their consent.
- Be mindful of noise levels and avoid disturbing others.
Compliance with Regulations
Understanding and adhering to local laws is mandatory.
- Register your drone if required by your local regulations.
- Check for temporary flight restrictions (TFRs) before each flight.
- Maintain awareness of no-fly zones.
Safe Operating Distances
A visual representation (described) illustrating safe distances.
Imagine a diagram showing a drone at the center. Circles radiating outwards represent increasing distances. The innermost circle, perhaps 5 meters in radius, is labeled “No people allowed.” The next circle, maybe 15 meters in radius, is labeled “Keep a safe distance.” Beyond this circle, the diagram could show other potential hazards, like tall buildings, marked with their respective safe distances.
The diagram visually emphasizes the need to maintain safe operating distances from people and obstacles.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational framework, equipping you with the knowledge to safely and responsibly operate a drone. Remember that consistent practice, coupled with a keen awareness of safety regulations and ethical considerations, is key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the learning process, and enjoy the incredible perspectives and possibilities that drone technology offers.
Essential Questionnaire
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’ve moved locations or experienced magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during a flight?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and return the drone to your location using visual cues. Prioritize a safe landing.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country/region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
What is the best way to store my drone batteries?
Store drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Keep them at approximately 50% charge when not in use for extended periods.
